Sequences
Sequences
A sequence is a list of numbers in a specified order. The different numbers occurring in a sequence are called the terms of the sequence.
Let the terms of a sequence be a1, a2, a3, …, an, …, etc.
The subscripts indicate the position of the term. That means,
First term = a1
Second term = a2
Third term = a3
….
The nth term is the number at the nth position of the sequence and is denoted by an. This term is also called the general term of the sequence.
Sequences Rules
All the terms of a sequence possess a certain rule upon which the successive terms are defined. In the above examples, the sequence 3, 9, 27, 81…,59049 indicates the rule as the powers of 3. Here, each succeeding number will be obtained by multiplying the previous term with 3. Similarly, the set of even numbers also contains a rule that each successive term is obtained by adding 2 to the previous term. Based on these rules, we can define the general term of the sequences. This can be done as given below:
Sequence 1: 3, 9, 27…., 59049
a1 = 3 = 31
a2 = 9 = 32
a3 = 27 = 33
Thus, an = 3n
So, the 10th term of the sequence = a10 = 310 = 59049
Also, this is a geometric sequence with common ratio r = 3.
Sequence 2: 2, 4, 6, ….
a1 = 2 = 2(1)
a2 = 4 = 2(2) Or a1 + 2
a3 = 6 = 2(3) OR a2 + 2
So, an = 2n Or an-1 + 2
Thus, it is an arithmetic sequence with common difference d = 2.
We can define the terms of a sequence using indexes while calculating the sum of the terms of the sequence using ∑ and the corresponding general term with suitable index numbers.
For example, the sum of the first 20 terms of the sequence 2, 4, 6, 8,… can be expressed as
. Here, “i” denotes the index of the sequence and 2n is the general term.
Sequences Examples
There are several patterns of numbers which can be considered as the examples of sequences with finite or infinite terms. They are given below along with the general terms and terms of the sequence:
Example 1: Set of Odd numbers greater than 1 forms a sequence with general term 2n + 1. The terms of this sequence are:
Thus, the sequence is: 3, 5, 7, 9,….
Example 2: The list of perfect squares or square numbers is an example of sequence with the general term n2.
The terms of this sequence are:
Thus, the sequence is: 1, 4, 9, 16,…
Example 3: Another example of sequences is the list of cube numbers or perfect cubes with the general term n3. The terms of this sequence are:
Thus, the sequence is: 1, 8, 27, 64,…
Example 4: One of the important examples of a sequence is the sequence of triangular numbers. They also form the sequence of numbers with specific order and rule.
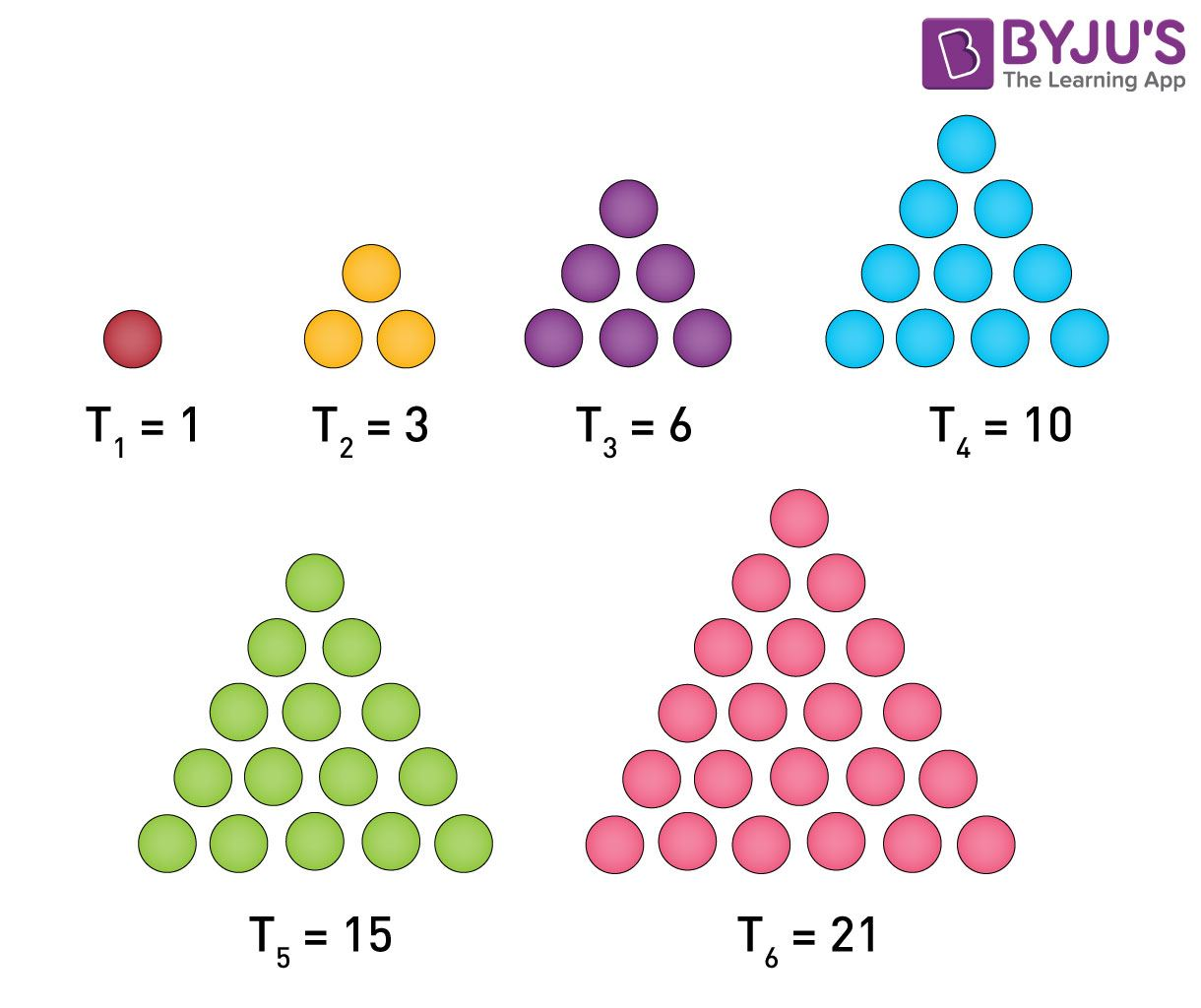
In some number patterns, an arrangement of numbers such as 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8,… has invisible pattern, but the sequence is generated by the recurrence relation, such as:
a1 = a2 = 1
a3 = a1 + a2
an = an – 2 + an – 1, n > 2

Informative and well-organized. The examples you used made it easier to understand the patterns and formulas involved.
ReplyDeleteThank you Sir/Madam for a nice comment now I'm surely and interested to teach more about Mathematics.
DeleteWell approached
ReplyDeleteIncredible work, you've truly captured something special here
ReplyDeleteinteresting
ReplyDelete